Formnext 2024: The Role of 3D Printing in Space Exploration;
One of the most significant events in additive manufacturing, Formnext 2024, stood out this year with its focus on innovations in the space sector. While previous years highlighted automotive and sustainability projects, this year’s exhibition turned its spotlight on advanced topics such as metal printing technologies and space applications. From spacecraft components to in-situ manufacturing with local materials in space, the event covered a wide range of groundbreaking developments.
Manufacturing in Space with 3D Printing
In-space manufacturing holds immense potential for reducing logistical costs and ensuring sustainability in long-term exploration missions. By enabling the production of lightweight, durable components with complex designs, 3D printing plays a pivotal role in space missions.
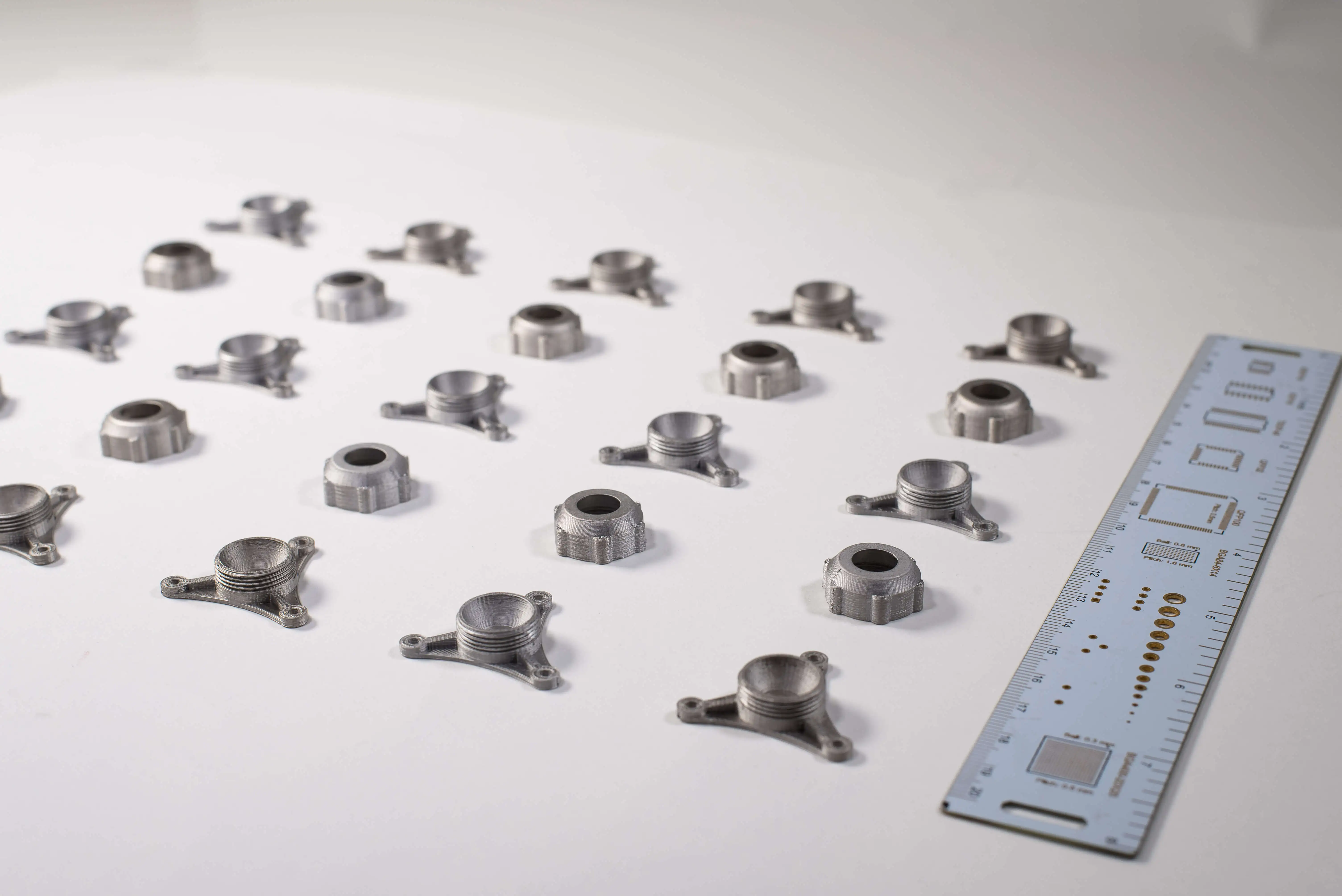
Key highlights include: Complex Components: Detailed parts such as rocket engine thrusters, combustion chambers, injector heads, and cooling channels can be produced in a single manufacturing step.
Utilizing Local Materials: The ability to manufacture directly in space using local resources, such as regolith on Mars or the Moon, reduces logistical costs and lays the foundation for sustainable infrastructure for long-term missions.
This innovative approach makes the manufacturing process more flexible and economical, opening new doors for scientists and engineers.
DMLS and DED: Advanced Printing Techniques
Among the most popular methods for space applications were Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) and Direct Energy Deposition (DED), both of which garnered significant attention.
DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering):
• Enables the production of complex geometries in a single step.
• Creates lightweight, high-strength components.
DED (Direct Energy Deposition):
• Ideal for repairing or modifying existing components.
• Demonstrated success in projects like the coating of Ariane 6 rocket engines.
Ponticon GmbH achieved notable success by using DED technology for the Ariane 6 engine coating. The precise melting of metal powder mid-air reduced costs and overcame technical challenges
Advanced Materials for Space Exploration
Material selection is critical in space research to balance durability and cost-effectiveness. Formnext 2024 showcased several innovative materials:
Copper Alloys: Essential for rocket components due to their high thermal conductivity.
Nickel-Based Superalloys: Preferred for engine and propulsion systems thanks to their high-temperature resistance.
PEEK and Regolith-Based Composites: Offer low-cost solutions meeting NASA's standards for radiation and chemical resistance.
Silicon-Based Materials: Introduce a sustainability-focused approach by minimizing waste.
These materials are transforming production processes by offering durable, lightweight, and cost-effective solutions for space exploration.
Challenges and Future Opportunities
Despite its transformative potential, space-based 3D printing still faces several key challenges:
High Costs: Materials used in printing processes remain expensive, with more than 60% of total costs attributed to materials for projects like the Ariane 6 engine coating.
Complex Geometries: Producing intricate components such as cooling channels presents ongoing technical hurdles.
Process Optimization: There is a need for faster and more efficient printing methods.
Nonetheless, groundbreaking projects like the LEAP 71 engine and the world’s largest metal-printed rocket motor showcased at the event prove that progress is not only possible but inevitable.
3D Printing's Contribution to Space Research
Formnext 2024 reaffirmed the critical role of 3D printing in space exploration. By leveraging lightweight materials, complex designs, and high-performance solutions, this technology is poised to transform not just manufacturing processes but also the dynamics of space exploration itself.
The future of in-space manufacturing and 3D printing centers on reducing logistical costs, advancing sustainability, and achieving technological breakthroughs. These developments provide scientists with the tools and opportunities to undertake bolder projects and push the boundaries of exploration further than ever before.