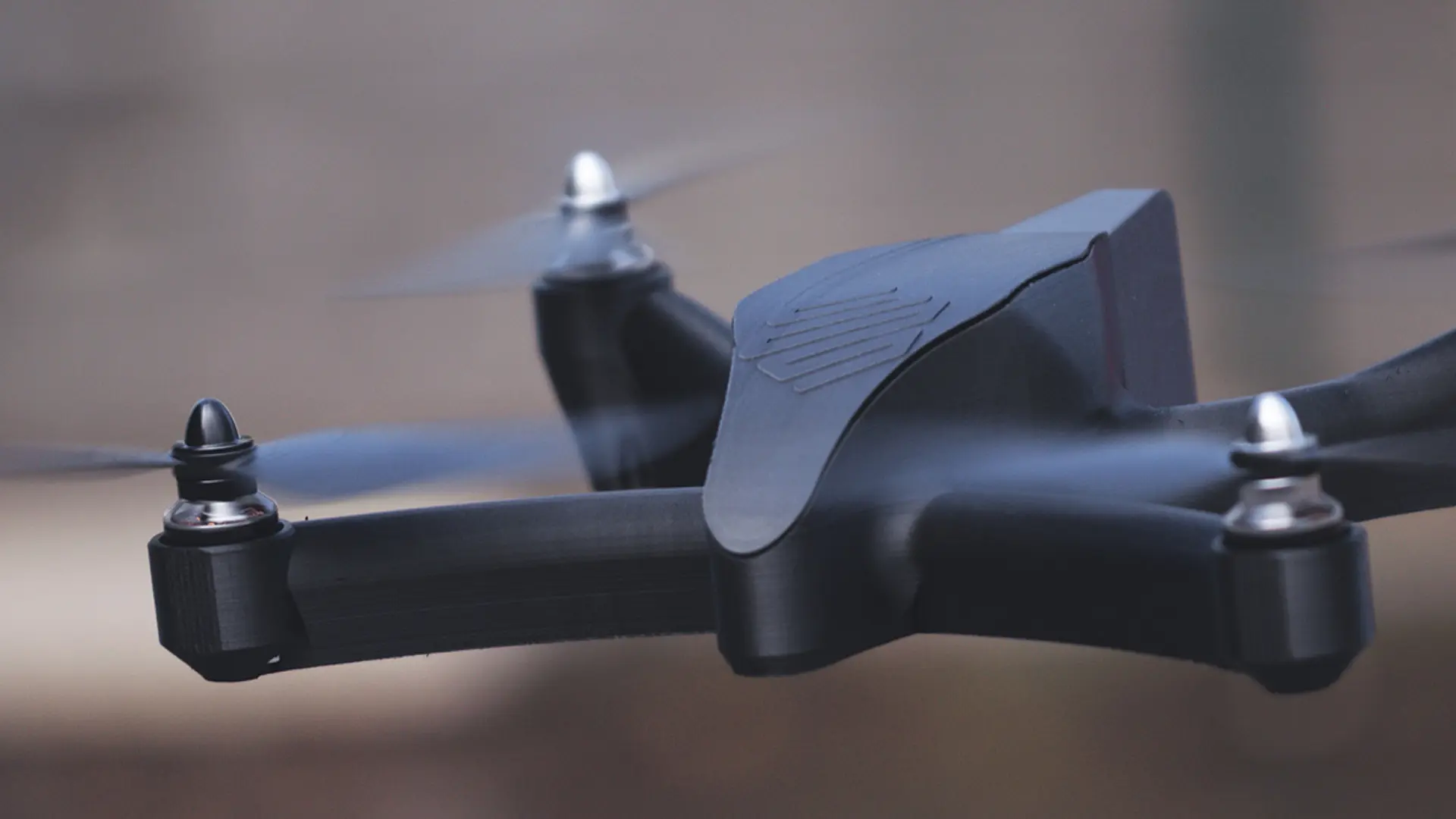
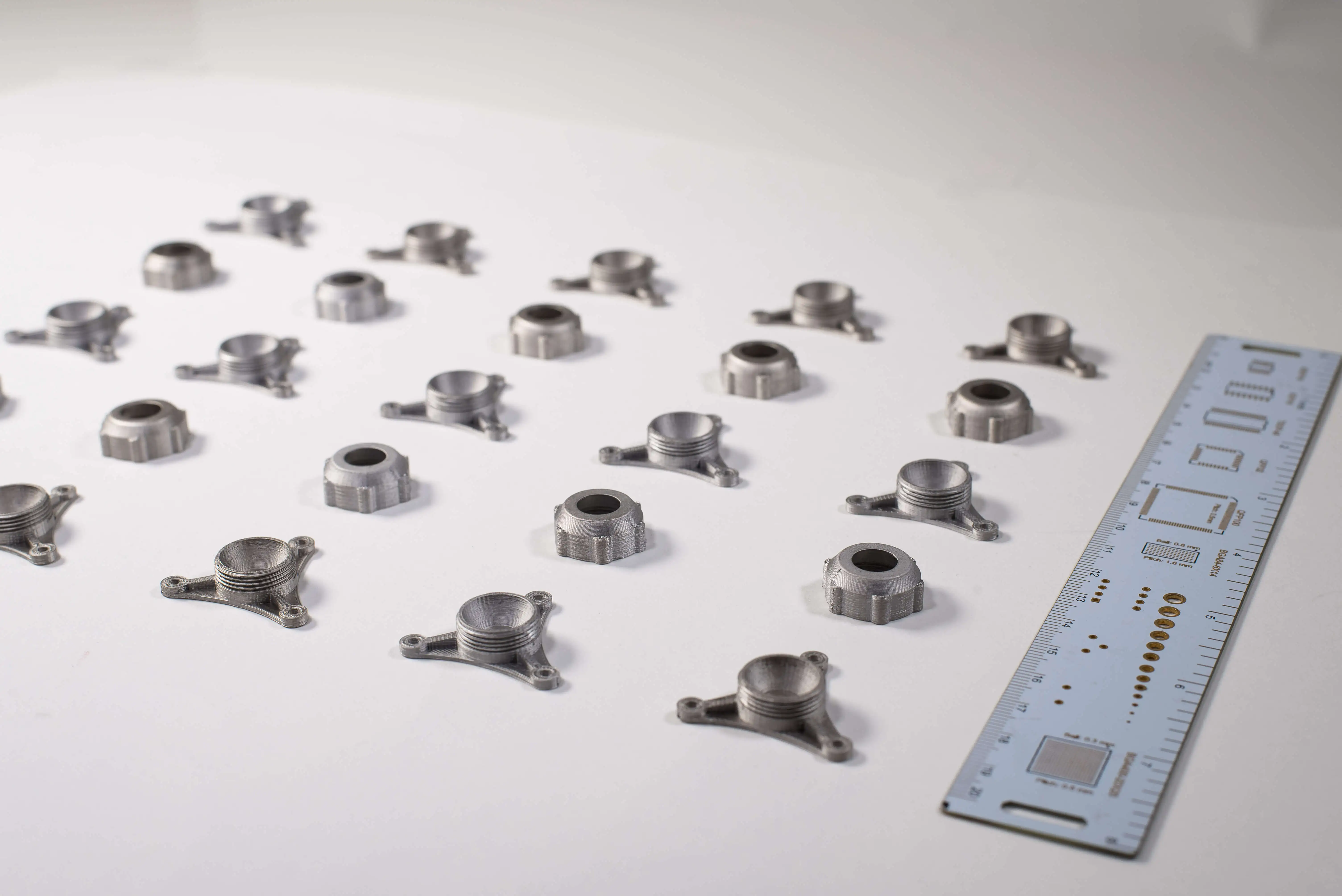
Application Areas of Additive Manufacturing: Defense, Aerospace, Automotive, and Robotics;
Advancing digital manufacturing technologies are rapidly transforming the global production ecosystem. At the core of this transformation lie additive manufacturing approaches, which are used across a wide spectrum from industrial design to mass production. High-precision sectors such as defense, aerospace, automotive, and robotics are expanding their capabilities thanks to the flexibility, speed, and cost advantages offered by this technology. This article provides a detailed explanation of how modern additive manufacturing is positioned today, based on scientific data and real industrial applications.
The Fundamentals of Additive Manufacturing and Its Place in the Industry (What is additive manufacturing?)
In engineering literature, the process known as Additive Manufacturing (AM) is based on the principle of adding material layer by layer to transform a digital model into a physical product. Unlike subtractive manufacturing, it increases productivity by adding rather than removing material.
Additive manufacturing provides major advantages in producing complex geometries. Reports published by organizations such as NASA, Airbus, and BMW show that lightweight and highly durable parts previously impossible or inefficient to produce can now be manufactured with AM technologies.
Professionals seeking more comprehensive technical information on additive manufacturing can benefit from the expertise offered by Prodigma, which provides up-to-date industrial applications focused on additive production.
Sectoral Impact of Modern Additive Manufacturing Technologies
With the acceleration of industrial modernization, additive manufacturing has evolved from a prototyping tool into a technology adapted for mass production. Today, these technologies can be applied to a wide range of materials including metals, polymers, ceramics, and composites.
Especially in aerospace and defense, advanced machines reduce production times by up to 60%, while increasing part strength (Source: https://www.nist.gov/). This figure is based on research conducted by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Next-Generation Additive Manufacturing Techniques in Defense and Aerospace
Defense and aerospace are sectors where safety requirements are the highest. Therefore, additive manufacturing plays a critical role in performance, weight optimization, and material durability.
Key applications in these sectors include:
- Lightweight metal components: Some titanium components used in the F-35 fighter jet are 40% lighter compared to conventional production.
- Rapid spare part production: Boeing manufactures nearly 70 different interior aircraft components using AM technologies (Source: Boeing Official Publications).
- Heat-resistant engine parts: Fuel injectors developed by GE Aviation allow 25 components to be consolidated into a single part through AM techniques. This has resulted in a 30% reduction in maintenance costs.
Advanced materials and production validation processes used in defense projects are thoroughly tested within additive manufacturing workflows. For specialized production requirements, companies can access expert support through Prodigma.
The Role of Digital Manufacturing in Automotive and Mobility Solutions
The automotive industry is one of the sectors that has successfully translated its prototyping transformation into mass production. Additive manufacturing is preferred for numerous reasons, including vehicle lightweighting, customization, accelerated testing processes, and cost reduction.
Use cases in automotive include:
- Prototyping: Ford Motor Company has reduced prototyping times by 70% in new vehicle development (Source: https://corporate.ford.com/).
- Vehicle customization: Driver-specific interior trim parts are widely used in sports cars.
- Electric vehicle components: AM enables the production of complex battery modules with heat-management structures.
- Spare parts logistics: Inventory costs are reduced while rare parts can be produced on demand.
By improving efficiency, additive manufacturing significantly contributes to the automotive supply chain.
Transformation of Production Processes in Robotics through Additive Design
Components used in robotics such as sensor housings, joints, grippers, and custom tooling typically have complex geometries. For this reason, additive manufacturing presents an ideal solution.
Advantages for robotics include:
- Rapid adaptation of components requiring mechanical compatibility
- Lightweight and durable materials for robot arms
- Cost advantages in modular robot designs
- Customized end-of-arm tooling (grippers) for industrial robots
Academic research conducted by the MIT Robotics Laboratory (https://www.mit.edu) shows that polymer grippers produced with AM are 50% lighter compared to those produced through conventional methods.
The Future of Additive Manufacturing and Its Impact on Digital Factories
As one of the foundational pillars of Industry 4.0, additive manufacturing enables full automation and flexible production lines when integrated with data-driven manufacturing approaches.
The key developments that will shape the future include:
- AI-assisted design optimization
- Real-time defect detection in production
- Higher strength standards in AM-produced metal alloys
- Fully digital supply chain management
- Energy-efficient production models
In the journey of digital transformation, Prodigma stands out by offering accurate guidance to companies. For projects requiring technical expertise, direct contact ensures access to professional support.
Additive Manufacturing is Setting New Standards for Industrial Transformation
Expanding its influence from defense and aerospace to automotive and robotics, additive manufacturing provides powerful solutions to the demands of modern industries for speed, cost efficiency, flexibility, and quality. Supported by academic research, this technology gives companies a competitive edge while pushing engineering applications toward more innovative solutions.
Businesses aiming to take part in the future of manufacturing should combine the right technology with specialized expertise. The professional solutions offered by Prodigma can help you build a more flexible, faster, and more efficient production model.
A small step today could be the beginning of a powerful transformation that defines tomorrow’s manufacturing standards.